ESTJ | MBTI Personality Type
Information about the MBTI personality type ESTJ. Conscious cognitive functions, shadow cognitive functions, brain research, similar types, sex and population ratio and ESTJ memes, videos and more.
Table of Contents
Known As
The Executive
The Supervisor
The Overseer
1 Cognitive Functions
Conscious
Unconscious
Nemesis: Ti
Critic: Se
Trickster: Ni
Demon: Fe
What are the cognitive functions for ESTJ and what do they mean?
The Myers-Briggs Type Indicator (MBTI) is a widely used personality assessment tool basing it’s conscious cognitive functions on Carl Jung's theories of psychological types. The original test was developed by Katharine Cook Briggs and her daughter Isabel Briggs Myers during the mid-20th century.
The MBTI framework is built upon four pairs of dichotomies, resulting in 16 possible personality types. Extraversion (E) vs. Introversion (I), Sensing (S) vs. iNtuition (N), Thinking (T) vs. Feeling (F), and Judging (J) vs. Perceiving (P).
Later on, other psychologists and researchers have added to the original Carl Jung framework alongside Katharine Cook Briggs and Isabel Briggs Myers, such as the psychologist John Beebe and author Linda Berens. Beebe and Berens have developed what is known as the shadow cognitive functions which are the parts of one’s personality which often arise under stress or during times of personal growth.
For pages discussing the scientific validity of MBTI, it’s comparison to the big 5 and other psychology tests, checkout this page: About.
2 Type group
Sentinels
The Sentinels group is made up of Introverted Sensing dominant or auxiliary users.
They are ESTJ, ISTJ, ESFJ and ISFJ.
This is a group of people who want to help organise the world.
For more information about the Sentinels, checkout their article:
3 Mistypes
Te dominant: ESTJ vs ENTJ
ENTJ vs ESTJ - Type Comparison by Cognitive Personality
The 16 Personalities and their Common Mistypes by Love Who
Si Auxiliary: ESTJ vs ESFJ
-
4 Statistics
ESTJ is 8% of the population with a sex ratio of Male: 65% and Female: 35%.
In the overall population, ESTJ is 10.6% of men and 5.6% of women.
For more information about this checkout: Statistics.
5 Brain Research
An ESTJ’s brain, as researched in Dario Nardi’s university research lab, shows:
A full breakdown of the regions can be seen here:
6 Similar but Different
ISTP: Ti-Se-Ni-Fe
ESTJ likes what ISTP likes in the same amounts but for different reasons.
(Te-Si-Ne-Fi vs Ti-Se-Ni-Fe).
INFP: Fi-Ne-Si-Te
ESTJ appreciates INFP for wanting to do what they naturally want to avoid doing.
(3rd-4th tier weaknesses Te-Si-Ne-Fi vs Fi-Ne-Si-Te).
ENFJ: Fe-Ni-Se-Ti
ESTJ appreciates ENFJ for their skills being the total polar opposite to theirs and vice versa.
(7th-8th tier weaknesses Te-Si-Ne-Fi-Ti-Se-Ni-Fe vs Fe-Ni-Se-Ti-Fi-Ne-Si-Te).
7 Enneagram
Type 1, Type 3, Type 6, Type 8, Type 2
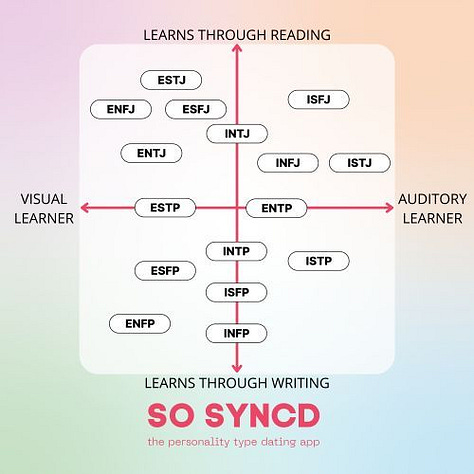
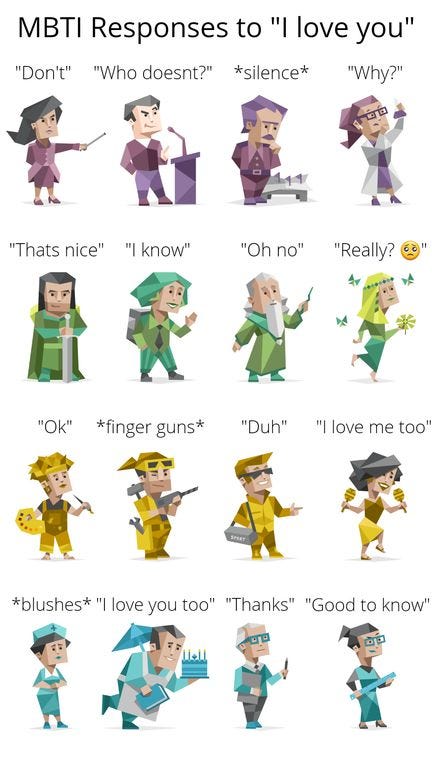
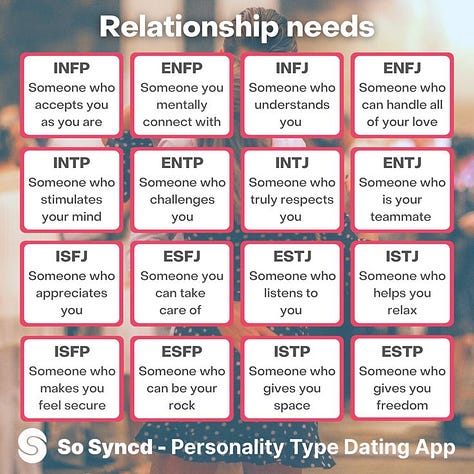
8 Memes
Group







Individual
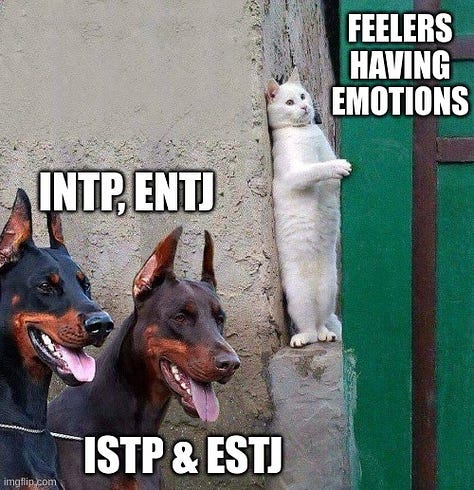




Romance



9 Videos
Inside The Mind Of The ESTJ (+ playlist) by Love Who
Primary (Hero): Te
Auxiliary (Parent): Si
Tertiary (Child): Ne
Inferior: Fi
Nemesis: Ti
Critic: Se
Trickster: Ni
The 16 Type's - Worst Functions by Love Who
Demon: Fe
10 Bibliography
Storm, Susan. November 15, 2019. "How Rare Is Your Myers-Briggs® Personality Type?" Psychology Junkie. Link (archive).
James, Frank. September 13, 2021. "Is INFJ STILL the Rarest of the 16 Personalities? (NEW Statistics)." YouTube. Link (archive).
James, Frank. September 20, 2021. "What Are the Rarest 16 Personalities Types in Men vs Women?" YouTube. Link (archive).
Isabel Briggs Myers, Mary H. McCaulley, Naomi L. Quenk, and Allen L. Hammer. 2018. "MBTI® Manual for the Global Step I™ and Step II™ Assessments 4th Ed - PDF." The Myers-Briggs Company. Link (archive).
Isabel Briggs Myers, Mary H. McCaulley, Naomi L. Quenk, and Allen L. Hammer. 2018. "MBTI® Manual for the Global Step I™ and Step II™ Assessments 4th Ed - PDF." Library of Congress Catalog. Link (archive).
Nancy A. Schaubhut, Richard C. Thompson, Michael L. Morris, Justin J. Arneson. 2019. "Germany (German) Supplement to the MBTI® Manual for the Global Step I™ and Step II™ Assessments." The Myers-Briggs Company. Link (archive).
Isabel Briggs Myers, Mary H. McCaulley, Naomi L. Quenk, and Allen L. Hammer. 1998. "MBTI manual: a guide to the development and use of the Myers-Briggs Type Indicator 3rd ed." Open Library. Link (archive).
Nardi, Dario. January 1, 2011. "Neuroscience of Personality: Brain Savvy Insights for All Types of People." Goodreads. Link (archive).
Nardi, Dario. January 1, 2011. "Neuroscience of Personality: Brain Savvy Insights for All Types of People." PDF Room. Link (archive).
Personality Studies. January 31, 2016. "MBTI’s Highest Activity Regions on Electroencephalogram (EEG)." Link (archive).
5wings4birds. January 9, 2023. "Data from Neuroscience of Personality by Dr.Dario Nardi for those saying that MBTI is just like @str0l0gy . Very interesting!" Link (archive).
Love Who. November 10, 2024. "I Analysed EVERY Enneagram & 16 Personalities Combination." YouTube. Link.
Group
1 - 9
10 - 19
Individual
Link (archive).
Link (archive).
Link (archive).
Link (archive).
Romance
Romance
1 – 9
ESTJ x . Link (archive).
ESTJ x . Link (archive).
ESTJ x . Link (archive).
ESTJ x . Link (archive).
ESTJ x . Link (archive).
ESTJ x . Link (archive).
ESTJ x . Link (archive).
ESTJ x . Link (archive).
ESTJ x . Link (archive).
10 - 16
ESTJ x . Link (archive).
ESTJ x . Link (archive).
ESTJ x . Link (archive).
ESTJ x . Link (archive).
ESTJ x . Link (archive).
ESTJ x . Link (archive).
ESTJ x . Link (archive).
How To Spot an ESTJ in 2 Minutes... by Love Who
Inside The Mind Of The ESTJ (+ playlist) by Love Who
The Sixteen Types: ESTJ by Michael Pierce
Revisiting the Types: ESTJ by Michael Pierce
ESTJ Personality Type in a Nutshell by It's Just Kevin
ESTJ personality type explained 🤣 by MBTI Humans
The 16 Personality Types - Best of ESTJ #1 by It's Just Kevin
3 things ESTJs think is normal (but isn’t) by Joyce Meng
16 Personalities Through the Eyes of the ESTJ by dear Kristin
ESTJ tier-ranking the 16 personalities by dear Kristin
Primary (Hero): Te
Te (Extroverted Thinking) - How does it show up in your Cognitive Stack? by Personality Guy
ENTJ and ESTJ: Te Hero (Extroverted Thinking) by Type Cast Heroes
Auxiliary (Parent): Si
ESTJ and ESFJ: Si Parent (Introverted Sensing) by Type Cast Heroes
Tertiary (Child): Ne
ESTJ and ESFJ: Ne Child (Extroverted Intuition) by Type Cast Heroes
Inferior: Fi
The 16 Personalities' 4th Function Appearing as the Angel on Their Shoulder by dear Kristin
ENTJ and ESTJ: Fi Inferior (Introverted Feeling) by Type Cast Heroes
Nemesis: Ti
Critic: Se
Trickster: Ni
How Does Your Trickster Function Work? | EgoHackers by EgoHackers
Demon: Fe





