ENTP | MBTI Personality Type
Information about the MBTI personality type ENTP. Conscious cognitive functions, shadow cognitive functions, brain research, similar types, sex and population ratio and ENTP memes, videos and more.
Table of Contents
Known As
The Debator
The Inventor
1 Cognitive Functions
Conscious
Unconscious
Opposing: Ni
Critic: Te
Trickster: Fi
Devil: Se
What are the cognitive functions for ENTP and what do they mean?
The Myers-Briggs Type Indicator (MBTI) is a widely used personality assessment tool basing it’s conscious cognitive functions on Carl Jung's theories of psychological types. The original test was developed by Katharine Cook Briggs and her daughter Isabel Briggs Myers during the mid-20th century.
The MBTI framework is built upon four pairs of dichotomies, resulting in 16 possible personality types. Extraversion (E) vs. Introversion (I), Sensing (S) vs. iNtuition (N), Thinking (T) vs. Feeling (F), and Judging (J) vs. Perceiving (P).
Later on, other psychologists and researchers have added to the original Carl Jung framework alongside Katharine Cook Briggs and Isabel Briggs Myers, such as the psychologist John Beebe and author Linda Berens. Beebe and Berens have developed what is known as the shadow cognitive functions which are the parts of one’s personality which often arise under stress or during times of personal growth.
For pages discussing the scientific validity of MBTI, it’s comparison to the big 5 and other psychology tests, checkout this page: About.
For ENTP, it’s cognitive functions of Ne-Ti-Fe-Si in the conscious and Ni-Te-Fi-Se in the unconscious create an interesting variation of person.
This combination results in ENTP encountering random new details (Ne) then going through analysis and systematic storage of the data (Ti). The data they accumulate is seen through the lens of it's usefulness for people or its origins being from other people (Fe). This enables ENTP to assess the emotions of others and navigate group dynamics effectively by providing unique useful data (Ne-Ti) catered specifically to individuals by distinguishing them from each other (Fe).
For more details on how each cognitive function works, checkout the individual pages: Ti.
2 Type Group
Analysts
The Analysts group is made up of Thinking + Intuition as dominant or auxiliary users.
They are ENTJ, INTJ, ENTP and INTP.
This is a group of people who want to seek out and find use for new facts.
For more information about the Analysts, checkout their article:
3 Similar types
Ne Dominant: ENTP vs ENFP
ENFP vs ENTP - Type Comparison by Cognitive Personality
The 16 Personalities and their Common Mistypes by Love Who
To learn more about ENTP and ENFP, see here; ENTP vs ENFP.
For examples of ENTP and ENFP contrasting Ti and Te, go to the page for Ti.
Ti Auxiliary: ENTP vs ESTP
The 16 Personalities and their Common Mistypes by Love Who
The Definitive Video: Ne vs. Se (Extroverted Intuition vs. Extroverted Sensing) by Type Cast Heroes
The differences between ENTP and ESTP is within their primary Extraverted Perceiving functions, Ne (Extraverted Intuition - ENTP) and Se (Extraverted Sensing - ESTP). The two functions shape how individuals engage with the external world.
Ne generates diverse possibilities and connections from current observations, fostering innovative ideas. However, Ne users may struggle to narrow down options or sustain focus on one idea.
Se, on the other hand, keenly observes and reacts to the immediate environment, thriving in the present moment. Se users excel at adapting to changing circumstances but might overlook future consequences.
Both functions prioritise real-time interactions, offering unique strengths and challenges in their cognitive function stack.
4 Statistics
ENTP is 3% of the population with a sex ratio of Male: 70% and Female: 30%.
In the overall population, ENTP is 4.3% of men and 1.8% of women.
5 Brain Research
An ENTP’s brain, as researched in Dario Nardi’s university research lab, shows:
A full breakdown of the regions can be seen here:
6 Similar but different
INTJ: Ni-Te-Fi-Se
ENTP likes what INTJ likes in the same amounts but for different reasons.
(Ne-Ti-Fe-Si vs Ni-Te-Fi-Se).
ISFJ: Si-Fe-Ti-Ne
ENTP appreciates ISFJ for wanting to do what they naturally want to avoid doing.
(3rd-4th tier weaknesses Ne-Ti-Fe-Si vs Si-Fe-Ti-Ne).
ESFP: Se-Fi-Te-Ni
ENTP appreciates ESFP for their skills being the total polar opposite to theirs and vice versa.
(7th-8th tier weaknesses Ne-Ti-Fe-Si-Ni-Te-Fi-Se vs Se-Fi-Te-Ni-Si-Fe-Ti-Ne).
7 Enneagram
Type 7, Type 8, Type 5, Type 3




Individual
Romance









9 Videos
ENTP highlights in under 1 minute by Personality Guy
16 Personalities Through the Eyes of the ENTP by dear Kristin
Primary (Hero): Ne
ENFP and ENTP: Ne Hero (Extroverted Intuition) by Type Cast Heroes
Auxiliary (Parent): Ti
16 Types Cognitive Function Axes: Ti & Fe | (INTP, ENTP, ISFJ, ESFJ, ISTP, ESTP, INFJ & ENFJ) by Love Who
Tertiary (Child): Fe
Inferior: Si
Opposing: Ni
Critic: Te
Trickster: Fi
The 16 Type's - Worst Functions by Love Who
Devil: Se
10 Bibliography
Storm, Susan. November 15, 2019. "How Rare Is Your Myers-Briggs® Personality Type?" Psychology Junkie. Link (archive).
James, Frank. September 13, 2021. "Is INFJ STILL the Rarest of the 16 Personalities? (NEW Statistics)." YouTube. Link (archive).
James, Frank. September 20, 2021. "What Are the Rarest 16 Personalities Types in Men vs Women?" YouTube. Link (archive).
Isabel Briggs Myers, Mary H. McCaulley, Naomi L. Quenk, and Allen L. Hammer. 2018. "MBTI® Manual for the Global Step I™ and Step II™ Assessments 4th Ed - PDF." The Myers-Briggs Company. Link (archive).
Isabel Briggs Myers, Mary H. McCaulley, Naomi L. Quenk, and Allen L. Hammer. 2018. "MBTI® Manual for the Global Step I™ and Step II™ Assessments 4th Ed - PDF." Library of Congress Catalog. Link (archive).
Nancy A. Schaubhut, Richard C. Thompson, Michael L. Morris, Justin J. Arneson. 2019. "Germany (German) Supplement to the MBTI® Manual for the Global Step I™ and Step II™ Assessments." The Myers-Briggs Company. Link (archive).
Isabel Briggs Myers, Mary H. McCaulley, Naomi L. Quenk, and Allen L. Hammer. 1998. "MBTI manual: a guide to the development and use of the Myers-Briggs Type Indicator 3rd ed." Open Library. Link (archive).
Isabel Briggs Myers, Mary H. McCaulley, Naomi L. Quenk, and Allen L. Hammer. 1998. "MBTI manual: a guide to the development and use of the Myers-Briggs Type Indicator 3rd ed." Internet Archive. Link (archive).
Nardi, Dario. January 1, 2011. "Neuroscience of Personality: Brain Savvy Insights for All Types of People." Goodreads. Link (archive).
Nardi, Dario. January 1, 2011. "Neuroscience of Personality: Brain Savvy Insights for All Types of People." PDF Room. Link (archive).
Personality Studies. January 31, 2016. "MBTI’s Highest Activity Regions on Electroencephalogram (EEG)." Link (archive).
5wings4birds. January 9, 2023. "Data from Neuroscience of Personality by Dr.Dario Nardi for those saying that MBTI is just like @str0l0gy . Very interesting!" Link (archive).
Love Who. November 10, 2024. "I Analysed EVERY Enneagram & 16 Personalities Combination." YouTube. Link.
Group
1 - 9
10 - 19
Individual
Romance
1 - 9
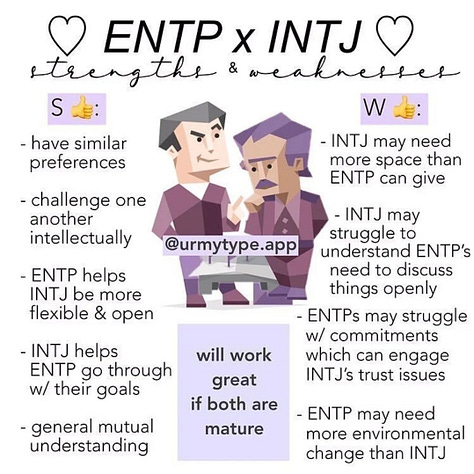
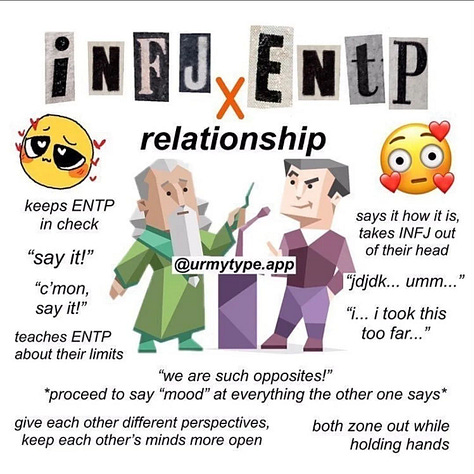
ENTP x INTJ. Link (archive).
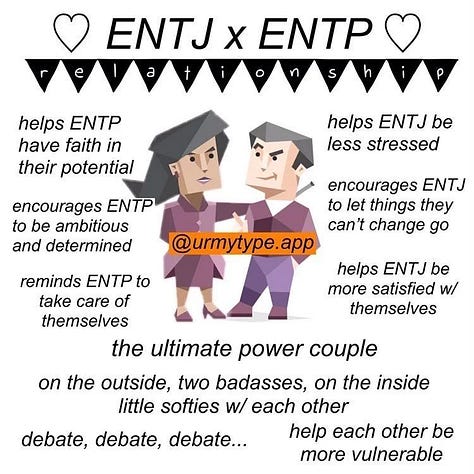
ENTP x ENTJ. Link (archive).
ENTP x ENFJ. Link (archive).
ENTP x ISFP. Link (archive).
ENTP x ESFP. Link (archive).
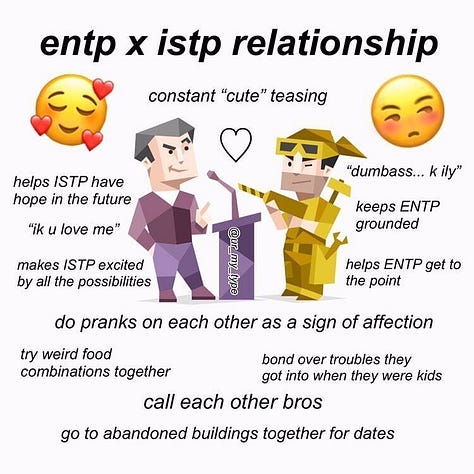
ENTP x ISTP. Link (archive).
ENTP x ESTP. Link (archive).
10 - 16
ENTP x ESTJ. Link (archive).
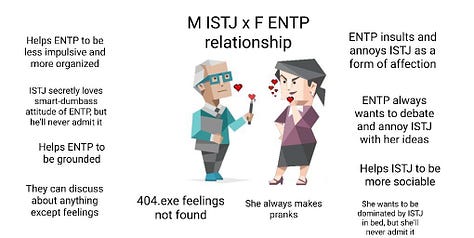
ENTP x ISFJ. Link (archive).
ENTP x ESFJ. Unable to source.
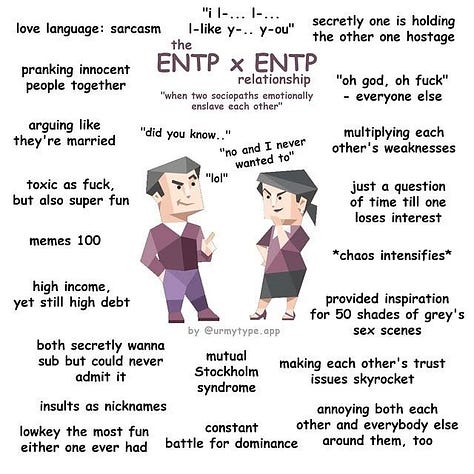
ENTP x ENTP. Link (archive).
How To Spot an ENTP in 2 Minutes... by Love Who
Inside The Mind Of The ENTP (+ playlist) by Love Who
The Sixteen Types: ENTP by Michael Pierce
Revisiting the Types: ENTP by Michael Pierce
ENTP Personality Type in a Nutshell by It's Just Kevin
Day in the life of an ENTP 🤣 by MBTI Humans
The 16 Personality Types - Best of ENTP #1 by It's Just Kevin
3 things ENTPs think are normal (but aren’t) #16types #entp by Joyce Meng
ENTP shots (playlist) by MBTI SHOTS
ENTP highlights in under 1 minute by Personality Guy
16 Personalities Through the Eyes of the ENTP by dear Kristin
ENTP tier-ranking the 16 personalities by dear Kristin
ENTP Girls Be Like... by Frank James
Primary (Hero): Ne
Ne Users often have Epiphanies #cognitivefunction #mbti #enfp #entp #infp #intp by Mind Maverick
ENFP and ENTP: Ne Hero (Extroverted Intuition) by Type Cast Heroes
Auxiliary (Parent): Ti
Ti and finding meaning | INTP ISTP ENTP ESTP by LiJo
ENTP and ESTP: Ti Parent (Introverted Thinking) by Type Cast Heroes
Tertiary (Child): Fe
Fe (extroverted feeling) display in your personality type (upper stack only) by Personality Guy
ENTP and ESTP: Fe Child (Extroverted Feeling) by Type Cast Heroes
Inferior: Si
The 16 Personalities' 4th Function Appearing as the Angel on Their Shoulder by dear Kristin
ENTP and ENFP: Si Inferior (Introverted Sensing) by Type Cast Heroes
Opposing: Ni
Critic: Te
Trickster: Fi
Fi in the Shadow Stack by Personality Guy
How Does Your Trickster Function Work? | EgoHackers by EgoHackers
Devil: Se





